Inelastic Collision Problems and Solutions Pdf
Submit the completed problem set to the lesson drop box. The second solution is the one of interest 2 v2 f v10.

Inelastic Collision Example Problem Physics Homework Help
Let object A be the bullet and object B be the block.
. A 10-gram bullet fired at 100 m s-1 collide a block of wood at rest. Inelastic relativistic collision A particle of mass m moving at speed v 4c5 collides inelastically with a similar particle at rest. The coefficient is 1 for an elastic collision less than 1 for an inelastic collision zero for a completely inelastic collision and greater than 1 for a superelastic collision.
P2 the momentum of the two balls after collision is given by. B What is its mass mC. Up to 24 cash back Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Worksheet p mv Show all work and circle your final answer.
Different kinds of collisions Collisions at an Angle problems involving collisions Elastic and Inelastic Collisions. The first is the trivial v2 f 0 which is just the initial state when the target is at rest. The 10 kg ball comes to a rest and the 8 kg ball begins to roll forward.
Let be the speed of the bullet before the collision and let V be the speed of the block with the bullet inside just after the collision. There are two types of collisions. Solution by Rudy Arthur.
Solution to Example 1. 50text kg 50 kg block at rest as shown in the above diagram. A 30-gram bullet moving at 30 ms collide a 1-kg block at rest.
The first ball moves away from the collision with a. After the collision the pair swings up to a maximum height of 0386 m. 400text ms 400 ms right after.
A What is the speed vC of the composite particle. Is a collision where the momentum of a system is conserved. Application of Newtons law of motion problems and solutions.
M 1 v 1i m 2 v 2i m 1 m 2v f v f m 1 v 1i m 2 v 2im 1 m 2 v f 1850 kg0 ms 975 kg220 ms north1850 kg 975 kg v f 759 ms to the north Problem 2 Two clay balls collide head-on in. PB mass velocity 02 5 1 Kgms. No credit will be given for work not shown.
After collision both truck and car move together at the same speed. Numerical Problems on Collisions Elastic inelastic collision 1 A block of mass m 1 is at rest on a long frictionless table one end of which is terminated in a wall. Use the equation for a perfectly inelastic collision.
Inelastic Collisions Notes and Problem Set As you work through the lesson complete the following problems. The truck and car collide and thereafter move as a single tangled mass. This is a conservation of momentum problem in which the total momentum of the glider at the beginning of the problem is equal to the sum of the momenta of the individual gliders at the end of the problem.
View Elastic Inelastic Solutionspdf from PHYSICS 1102 at Chattahoochee High School. Physics Tool box Completely Inelastic Collision Problem Solving Strategy sample exercise with solutions. Momentum of ball A.
This preview shows page 1 - 2 out of 3 pages. The ratio of kinetic energy after to kinetic energy before is evidently in this situation e2. In the special case of a one-dimensional elastic collision between masses m1 and m2 we can relate the final velocities to the initial velocities.
Each ball had a mass of 020 kg. Linear Momentum and Collisions Elastic and Inelastic Collisions Practice Problems 1. Mass of bullet m1 30 gram 003 kg Mass of block m2 1 kg Initial speed.
Conservation of energy applied to the motion of the block after the collision. Well only need to do one calculation for the total final kinetic energy. An example of this is can be observed in the case of a car collision where there is a large sound and the car body is deformed upon impact.
But its very important that you know the difference between the two and the main question to ask yourself is whether kinetic energy is conserved. If a ball falls on to a table from a height h0 it will take a time. Call the moving particle M and the particle at rest R the composite particle is defined.
The reason we get this solution is that the energy and momentum equations are the same if we reverse the direction of time change the direction of all velocities. Ek 1 2 mv21 2 57700 275 2218178125J218J Its obvious that after the collision there is considerably less kinetic energy than at the start. Just after the collision the bullet and the block move together as one mass at the same velocity.
In fact only about 0346 of the kinetic energy. Momentum of ball B. 2 In an inelastic collision total energy is still conserved but some kinetic energy is lost and transformed into energy in the form of sound thermal energy or permanent deformation of the objects.
First we need to decide if this is an elastic or. Suppose two balls have an elastic head-on collision during the act. A truck moves at 10 ms collide a car moves at 20 ms.
Conservation of momentum applied to the collision between the bullet and the block. Some of the worksheets below are Elastic and Inelastic Collision Problem Solving Worksheets Elastic and Inelastic Collisions. In both cases momentum must be conserved.
-24text ms 24 ms on the same road. Figure 838a is constant gives. State the law of conservation of momentum.
The collision is inelastic. Up to 24 cash back Holt McDougal Physics 1 Sample Problem Set I Momentum and Collisions Problem G ELASTIC COLLISIONS PROBLEM American juggler Bruce Sarafian juggled 11 identical balls at one time in 1992. Find the change in the kinetic energy of the system consisting of both vehicles.
P2 01 v1 02 v2. Another block of mass m 2 is placed between the first block and the wall and set in motion to the left with constant speed v 2iAssuming that all collisions are completely elastic find the value of m 2 for. Let p1 be the momentum of the two balls before collision.
Determine the velocity of the bullet just before impact. P1 pA pB 2 Kgms. This is an inelastic collision.
Determine the speed of the block if the bullet and the block lock together as a result of the collision. A 10 kg ball rolling a speed of 20 ms strikes an 8 kg ball at rest. PA mass velocity 01 10 1 Kgms.
For this problem a 00200 kg bullet collides with a 57500 kg pendulum. Mass of block is 490 gram. The result is v1f m 1 m2 m1 m2 v1i 2m 2 m1 m2 v2i 75 v2f 2m 1 m1 m2 v1i m 2 m1 m1 m2 v2i 76 This result can be useful in solving a problem where such a collision occurs but it is not a fundamental equation.
Determine the 8 kg balls velocity. The correct answer is e. There are two solutions.
AP Physics Practice Test Solutions. The bullet moves at.

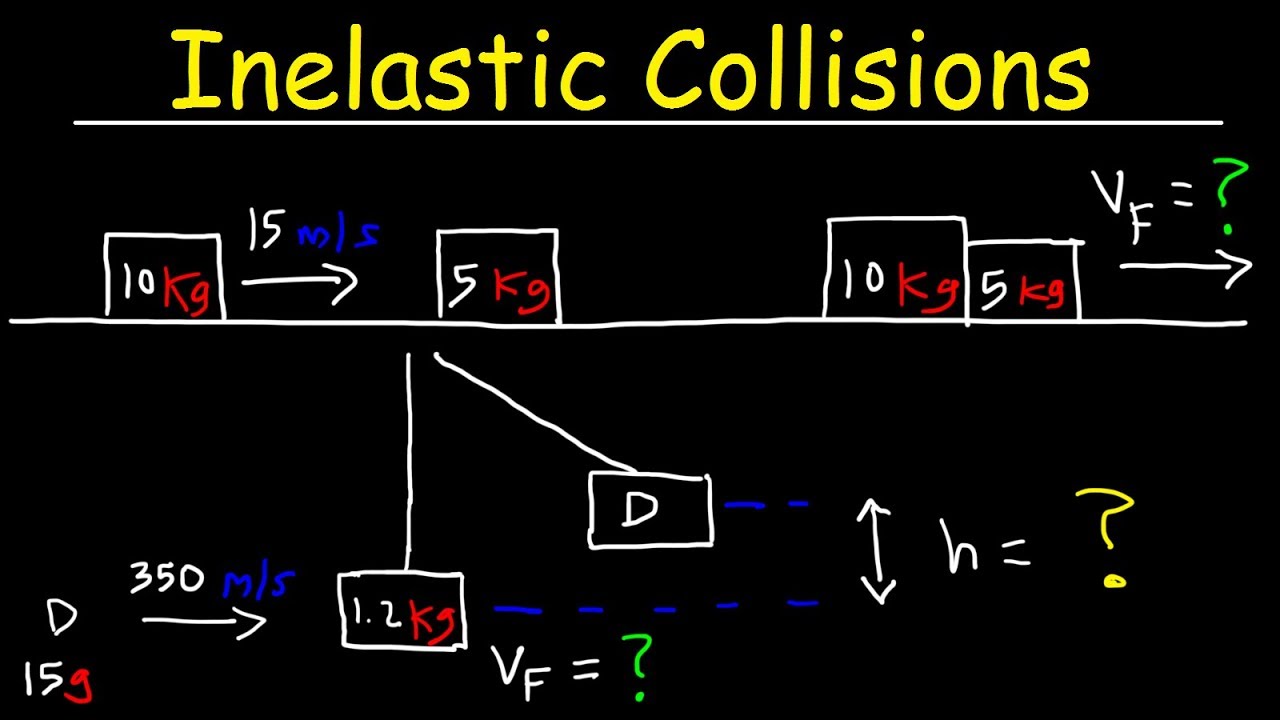
Inelastic Collision Physics Problems In One Dimension Conservation Of Momentum Youtube

What Is Inelastic Collision Definition Formula Examples

Question Exploration Conservation Of Momentum In Collisions Instructional Methods Ap Physics Critical Thinking Skills

Inelastic Collision Example Problem Physics Homework Help

Conservation Of Momentum Elastic And Inelastic Collision
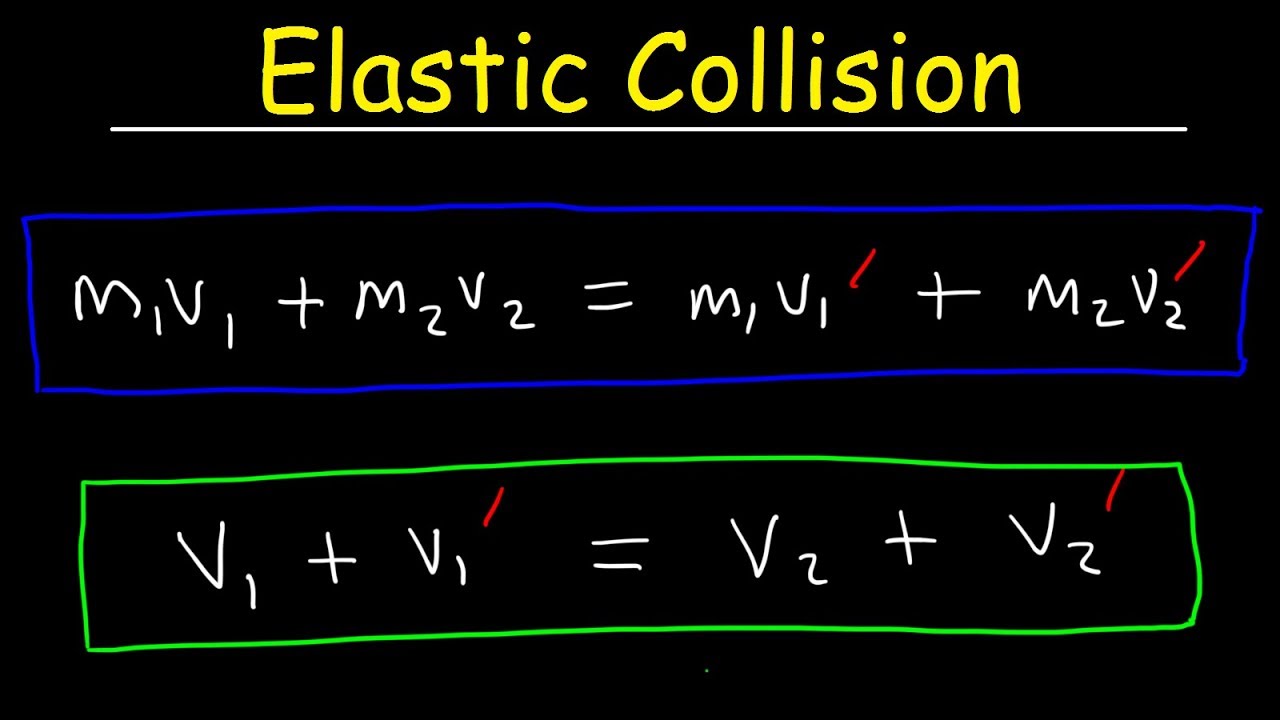
Elastic Collisions In One Dimension Physics Problems Conservation Of Momentum Kinetic Energy Youtube
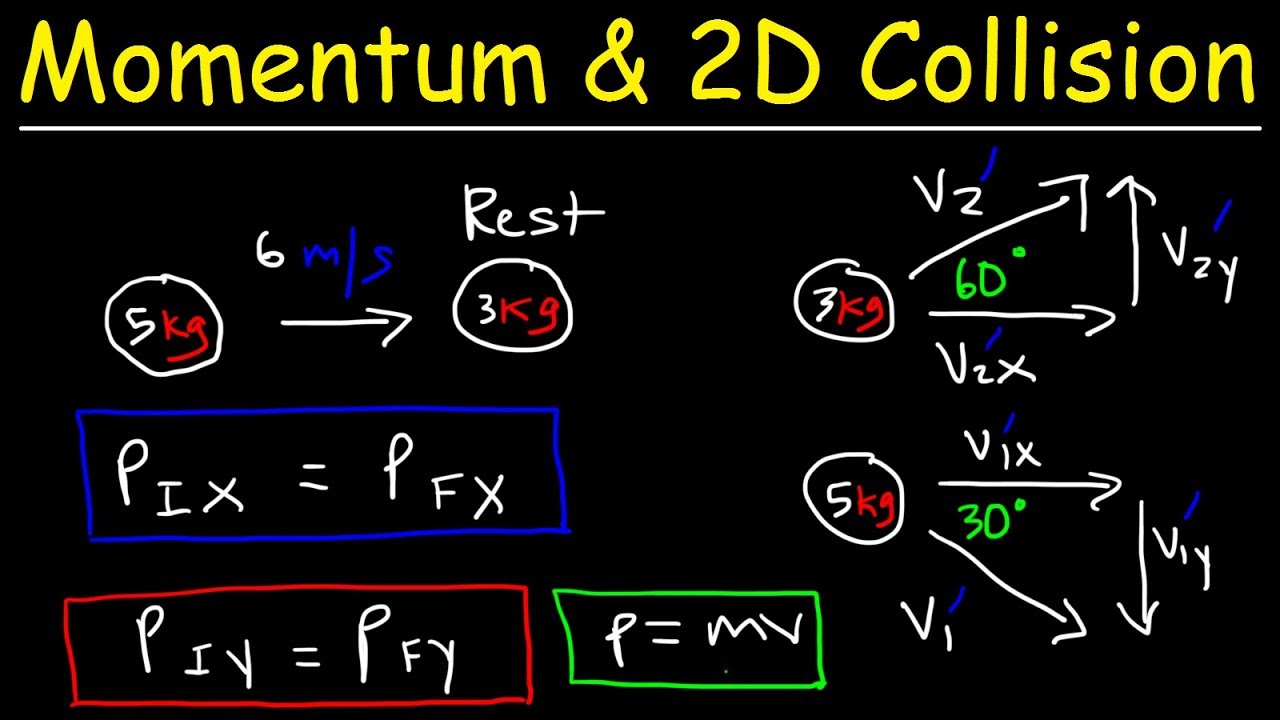
Conservation Of Momentum In Two Dimensions 2d Elastic Inelastic Collisions Physics Problems Youtube

Pdf Elastic Collisions In Minkowski Momentum Space With Lorentz Transformations

Inelastic Collision Example Problem Physics Homework Help

Powerpoint Of 3 Projectile Problems Physics Lessons Physics And Mathematics Guided Practice

The Ultimate Conservation Of Momentum Worksheet Amped Up Learning Writing Linear Equations Biology Worksheet Homework Worksheets

Elastic Collision Of Two Masses It Can Be Shown Exercise

Collision Elastic Inelastic Collisions In One And Two Dimensions Videos

Conservation Of Momentum Physics Free Momentum Physics Physics Lessons Physics

Scaffolded Momentum Practice Word Problem Worksheets Worksheets Word Problems

Comments
Post a Comment